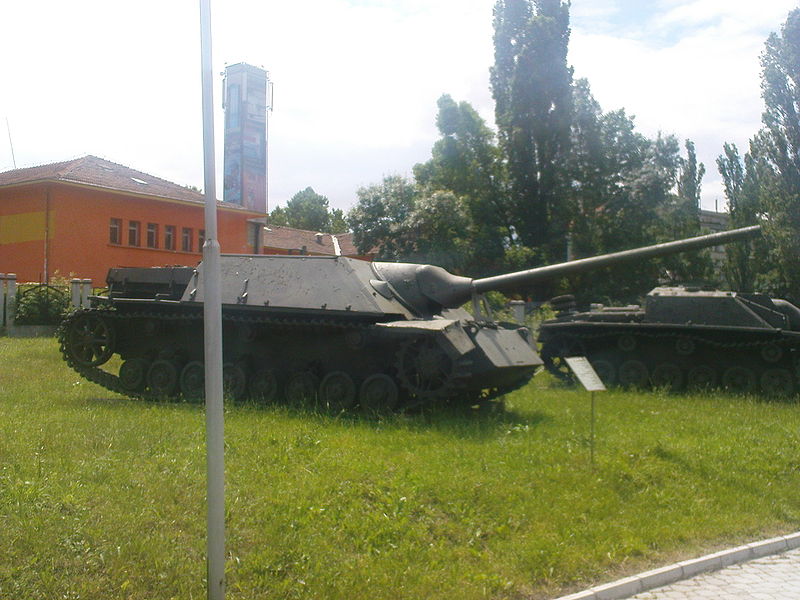
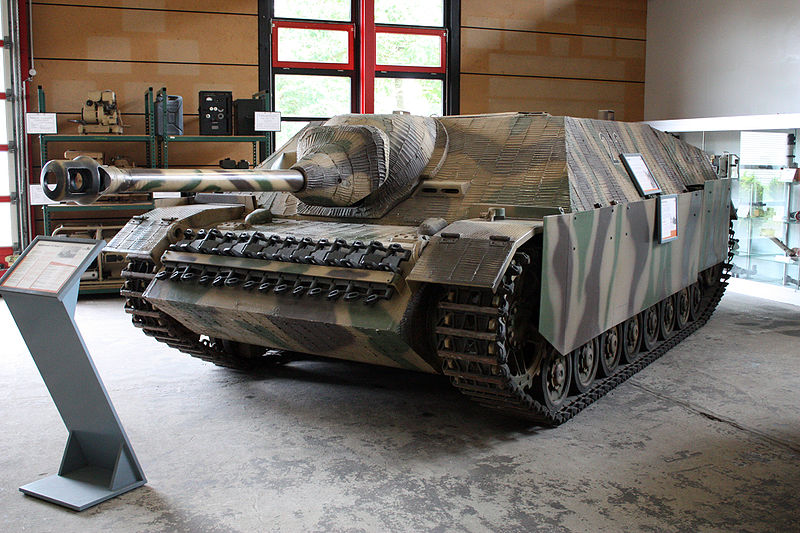
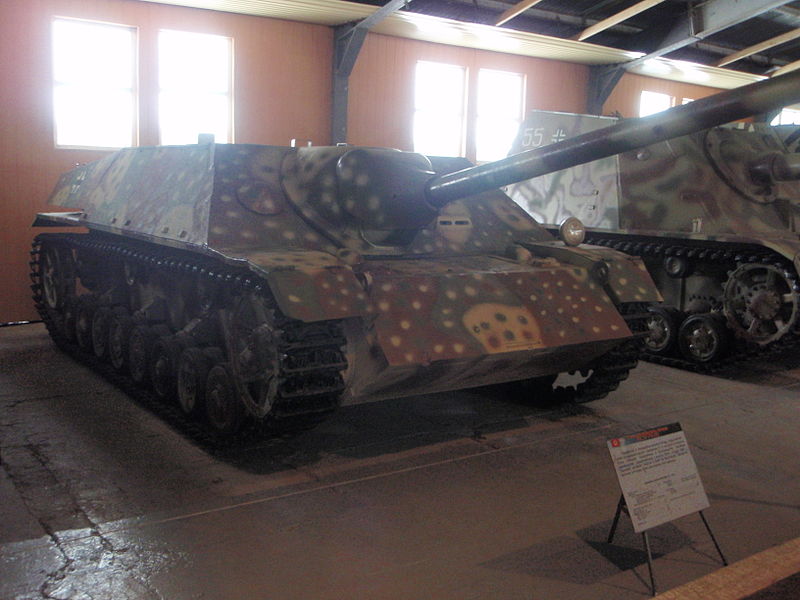
A new generation of tank hunters
The long tank hunter lineage, at first based on whatever chassis was available, like the Panzer I, II, Panzer 38(t), then the Panzer III and IV, drew heavily on the significant battlefield experience accumulated until 1943. At that time, this experience led to yet another generation of tank hunters, purpose-built, well armored, with a very low profile. This last generation encompassed the Jagdpanther, the Hetzer and a new vehicle proposed in mid-1943 by Vomag AG, based on the chassis of the Pz.Kpfw. IV. At first, this tank destroyer was named «neu Sturmgeschutz» (“new assault gun”), still classified as a self-propelled (AT) gun. The version that emerged for production was the Jagdpanzer IV Ausf.F, or Sd.Kfz.162, with a 7.5 cm Pak 39 L/48 main gun.
The main tank destroyer until then was the StuG III, but the decision to not build yet another tank hunter based on the Panzer III chassis was dictated by practical considerations. The latter chassis was not strong enough to carry longer guns and improved armor. The Panzer IV was, by then, produced in big numbers and, thanks to Albert Speer’s production management, simplified and cheaper.
Development
Hitler was shown the plans of the latest Sturmgeschutz auf Fahrgestell Pz.Kpfw.IV mit 7.5 cm KwK 42 L/70 on October 2, 1942. This tank destroyer had thicker armor compared to its predecessors, and the frontal armored plate was positioned at a steep angle. The 7.5 cm KwK 42 L/70 received a mask specifically shaped to fit in the frontal armor cutting, and was not fastened to the floor, as was customary with assault weapons. Hitler agreed that, before starting the full production with the long-barreled gun, the 7.5 cm Pak 39 L/48 was to be installed provisionally. In addition, he gave the order to abandon, in the shortest time possible, the old Pak 39 in favor of the long-barreled version. The wooden mock-up built by Voglandische Maschinenfabrik AG at Plauen, Saxony, was shown to the Führer on May, 05, 1943. The height of this mock-up was only 1720 mm, which was quite a low profile by the standards of the time. Another presentation was made on 20 October 1943 in East Prussia, this time with a steel prototype. Soon after, Hitler ordered a first batch of these tank destroyers to be built. Two modified Sd.Kfz.162 were equipped with the zero-series modified gun mask. They participated in trials in January 1944. Production really started in the summer of 1944.
Production & modifications
The peculiarity of the gun was that it was mounted in a spherical mask, that helped get rid of the usual complicated mechanism of vertical elevation. The frontal armor was a 80 mm (3.15 in) thick plate sloped at 15 degrees, which could withstand hits from the 76 mm (3 in) shells of American and Russian guns. The Vomag firm designed, in late 1943, two more layouts. The zero-series, in comparison with the serial production vehicles, had a different “pig-snout” mantlet shape and frontal armor rounded corners. During production, the armor plates were assembled in the same manner as for the Pz.Kpfw.IV, increasing the strength of their joints.
At first, there were no auxiliary weapons at all. The two slits on the front plate were modified as pistol ports, the right to fire a MG 42 machine gun, and the left for an assault rifle MP 44 or MP-40 sub-machine gun.
This tank destroyer reused almost everything from the Pz.Kpfw.IV, the body, running gear, engine and electrical equipment. Only the fuel tank position was altered, located under the gun and near to the radio operator. An additional fuel tank was located near the auxiliary two-stroke DKW engine, which powered the gun traverse. The crew compartment ventilation was also modified, mostly in connection to the brakes, which received an air stream from the engine compartment. The escape hatch position was also modified, relocated under the gunner’s seat. The armor was decreased eventually, to 60 mm (2.36 in) at the front, at an angle of 40°, which equivalated to 90 mm (3.54 in) of efective armor on the pre-production machines. In February 1944, 14 spare track pads fixations were added to the front beak. In the spring of 1944, spare parts were moved to the stern to lessen the load on the front of the suspension, and received another pair of spare rollers.
In March 1944, the left pistol port on the frontal armor was sealed. In March to early April, production vehicles received a special mount for a MG 42 on the cabin roof, which could be used remotely. As an alternative, a mask could be added for external use. Starting with chassis number 320301 Fgst, the frontal armor was increased from 60 to 80 mm (2.36-3.15 in), and 30 to 40 mm (1.18-1.57 in) on the sides. Until the end of May, all guns were fitted with a muzzle brake, but it was found during combat that these created a dust cloud, making it difficult to aim, and were just removed in the field. Spare road wheels were relocated and the periscope fixation was changed.
In the summer of 1944, the engine cooling system was protected by armored shutters.
The last modification was carried out in September 1944, when three all-metal support rollers replaced the rubberized ones. The Zimmerit coating was also abandoned. Some Jagdpanzer IVs were modified as Befehlswagen (command vehicles), with a crew of 5 and a radio FuG 8. The same month, two prototypes tested the fixed neu Starr 7.5 cm Pak 39 L/48, but similar issues were found as on the Jagdpanzer 38(t).
_Saumur-museum.jpg)
Design
Hull
The hull was made of homogeneous rolled armor plates welded together, of various thickness. Dortmunder-Huehler & Co in Kapfenberg and the steel foundry in Vítkovice were responsible for the armored plates, connected by joints at the edges, and then welded. At the front, left of the gearbox, sat the driver. Right-center was the crew/fighting compartment, the gunner also serving as the MG 42 machine gunner. On the left side stood the commander, and behind him the loader. Two single-piece round hatches were located above them in the roof. In the far right corner was located, over the gun breech, a small gas exhaust. The 44 cm evacuation hatch was located below the driver.
The standard radio transceiver FuG 5 SE10U was assisted by a 10 WSa (10-watt) or 10 WSb, with a range of 27.2 to 33.3 MHz. The transmitter also worked in the VHF range. There was an U 10a transformer and E Ua receiver. In phone mode, the range was 6400 m (4 mi), but it reached 9400 m (6 mi) when using Morse. It was installed on the right side, inside an anti-vibration housing, near the loader. The two-meter whip antenna was on the left side of the hull. A set of signal flags could be used and a 27 mm (1.06 in) flare pistol Walther LP/LP-42 was stored near the commander’s seat. In addition, the hull received tooling mounted on the rear engine plate, back plate and fenders. The fire extinguisher was located on the right and, later, toolboxes and fixtures were moved to the fender. The pick, shovel and crowbar were attached to the rear plate. The first aid kit and two hand-held fire extinguishers were stored inside the fighting compartment. The jack and the hand pump used for gasoline tanks were stored on the rear plate. On the back wall of the crew compartment there was an additional storage with canisters of water and gasoline, canvas covers, bucket and other equipment.
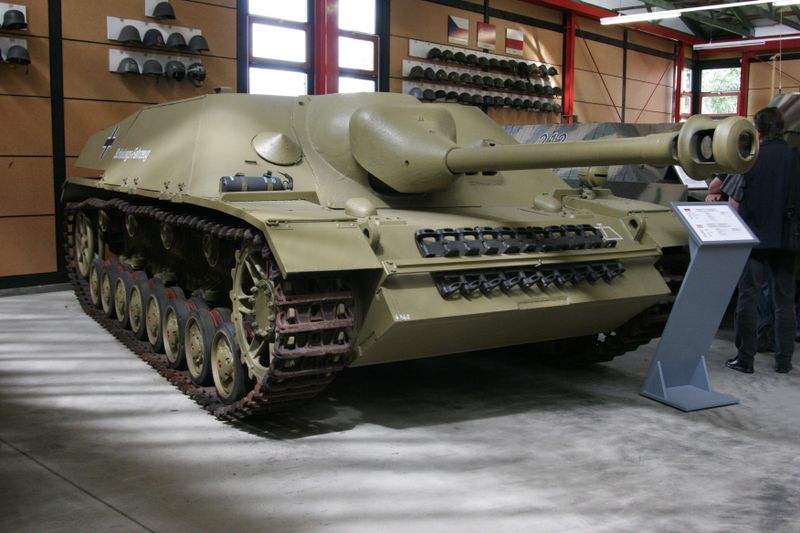
A Panzerjager IV/70(A), for “Alkett”, was a cheaper production version of the long barrel Jagdpanzer IV, now at the Saumur Museum in France. Notice the penetration hole from the shell that knocked out the tank.
Powerplant
The four-carburetor V-shaped 12-cylinder overhead valve Maybach HL 120 TRM engine was liquid cooled, built by Maybach Motorenwerke (Friedrichshafen), with Auto-Union AG (Chemnitz) components. The cylinder bore was 105 mm (4.13 in), stroke 115 mm (4.53 in), total displacement 11867 cm³, with alloy pistons of 0.12 to 0.16 mm course and compression ratio of 1:6.5. The top revolution speed was 3000 rpm, but the manual recommended was 2600 rpm. Maximum output was 221 kW (300 hp) and 195 kW (265 hp) at cruising speed. The torque was 2150 rpm for 80 micrograms. This gave a power to weight ratio of about 9.20 kW/ton or 12.5 hp/t. Two radiators (2.6 m2 surface) were located on the sides of the engine, with a forced circulation pump and a coolant operating at 80°. These vehicles were designed to operate on the Eastern Front and were equipped with a hot coolant system to assist starting in extreme cold. Air circulation was ensured with fans blowing Zyklon, each which two air filters.
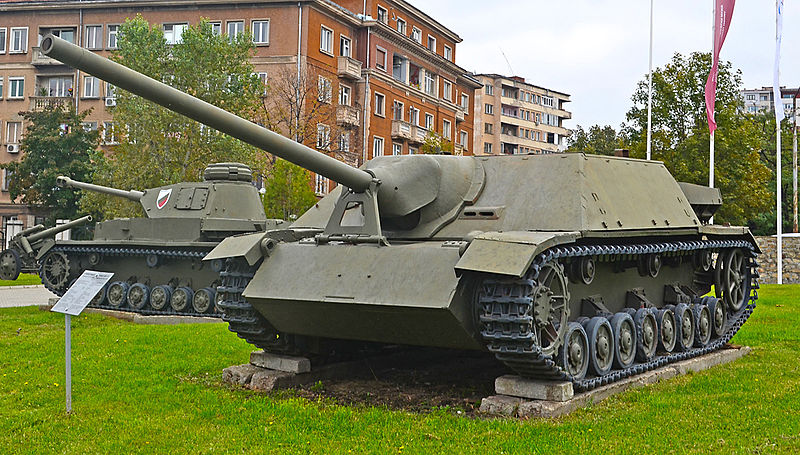

The filters were located on the right side of the engine compartment and powered by the engine. On late versions, they were closed with armored shutters. The air flow inside the engine compartment was directed out through the hull sides and blinds were coupled with a thermostat to regulate the flow. Three fuel tanks (74 octanes) had a total capacity of 470 liters and working capacity of 463 liters, whereas the fuel supply was provided by 2 Solex gas pumps and a manual emergency backup pump. The 3 tank levels were commonalized and the fuel selector was located on the driver’s instrument panel. Road consumption was 220 liters for 100 km and 360 liters cross country for the same distance. Oil tank capacity was 22 liters. The engine carburetors were Tina Solex 40JFF II and two drive shafts transmitted the torque to a dry clutch gearbox, three-disc, Fichtel & Sachs 120/HD. The ZF Aphon SSG76 planetary gearbox provided 6 speeds forward and one reverse. A lever placed to the right of the driver provided the steering, assisted by pedals and hydraulic transmission clutches. The planetary steering allowed to rotate tank destroyer on the spot and to brake. The gear ratio was 1:3.23 and the driving sprocket mechanical brakes were manufactured by Krupp.
The electrical system relied on a single-conductor wiring, 12 V, provided by a 600-watt generator Bosch GTLN 600/12-1500. Four extra Bosch 12B type 105 batteries gave 6 V, for a capacity 105 A/h. There were also two starter Bosch BNG 4/24 (24V output 2.9 kW) and aBosch W225N1 ignition candle. For the electronic ignition, cylinders could operate alternately and it was possible to start the engine with a simple twisted pen, handle inserted into the rear bottom armor plate opening. A no-delay Bosch AL/ZM I starter could be used in addition, or with the help of a Kubelwagen. These provided power for the lighting of the control devices, sight, crew compartment lights, roadlights (front left wing, protected), radio, machine gun elevation and Notek gun firing system.
Suspension
The suspension consisted of eight rubberized rollers arranged on four bogies, in pairs. The four return rollers were first rubberized, but became all-metal towards the end of the production. The drive sprocket was at the front and the track tensioner and steering wheel was the the rear of the drivetrain. The drive sprocket had 20 teeth. The tracks links were type Kgs 61/400/120, 400 mm wide, single-pin and made of manganese steel. The reference length for the ground contact track was 3520 mm. Each track was made of 99 links, manufactured at the Hamburg-based company Moorburger Trackenwerke. In autumn and winter, the tracks were swapped for the extended Ostenkette model which weighed 1750 kg (vs. 750 kg on standard tracks), meant to ease ground pressure on mud/snow.
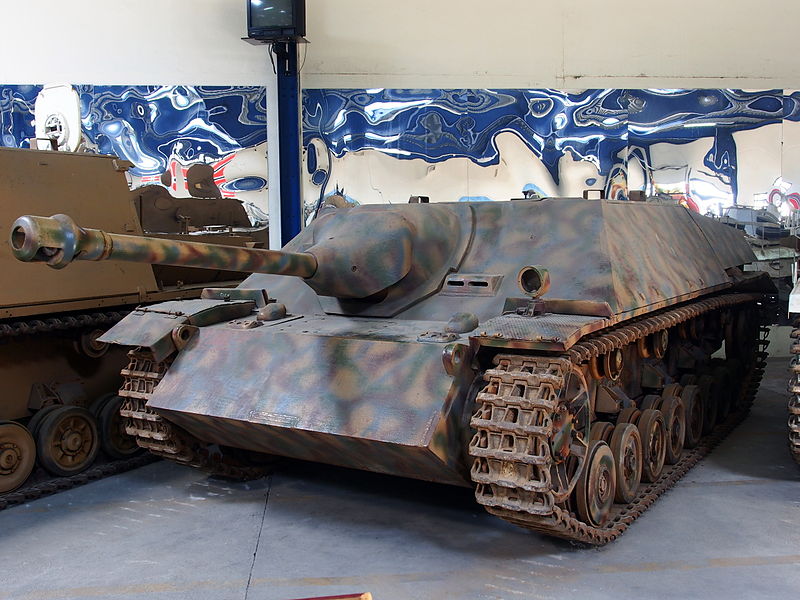

Jagdpanzer IV of the early production batches at the Saumur Museum.
Armament
The main gun, the 7.5 cm Pak 39 L/48, was assisted by a secondary 7.92 mm (0.31 in) MG 42, both served by electronic elevation at +15°/-5°, and traverse with an arc of fire of 20° on either side. The main gun sight was a telescopic Selbstfahrlafetten-Zielfernrohr la, with Carl Zeiss scopes, calibrated from 0 to 1,500 m (0-5000 ft) for the Pz.Gr.39 and 0 to 2,000 m (6500 ft) for the Pz.Gr.40. There was a 5x magnification 8° field of view. The MG 42 sight was a KZF 2 (1.8 x magnification, calibration up to 1200 meters range). The driver had a Fahrer 2 Winkelspiegel binocular periscope. The loader had a motionless Rblf 3b periscope and the commander had three Scherenfernrohr 14Z periscopes.
50% of the rounds stored were Pz.Gr.40 and 50% were Pz.Gr.39 armor-piercing. The ammunition (79 rounds) was located in the rear of the fighting compartment, near the fuel tanks, and under the gun on the right. The armor-piercing Pz.Gr.39 weighed 6.8 kg and its initial velocity was 790 m/s (2600 ft/s). It could defeat 108 mm (4.25 in) of armor at 30° at 100 meters, 96 mm (3.77 in) at 500 meters, 88 mm (3.46 in) at 1,000 meters and 64 mm (2.52 in) at 2,000 meters. Accuracy and first hit probability were 100% at less than 500 m and 97% at 1,000 m, with 77% at 1,500 m. The Pz.Gr.40, weighing 4.1 kg, had an initial velocity of 990 m/s (3250 ft/s). Its respective penetration values were 143 mm (5.63 in), 120 mm (4.72 in), 97 mm (3.82 in) and 77 mm (3.03 in) at the same ranges. The speed was taken in account when firing en route. Accuracy at 15 km/h (9 mph) decreased by 21% and by 33% at 25 km/h (16 mph), at ranges up to 500 m. The 7.92 mm (0.31 in) MG 42, located on the right of the gun, had 8 150 rounds canvas bags, but later these were kept in less sensitive duraluminium boxes. An additional 9 mm (0.35 in) MP 40 or an MP 44 7.92 mm (0.3 in) was also stored. Some carried a Nahverteidigungswaffe (16 x 27 mm grenade shrapnel launcher).
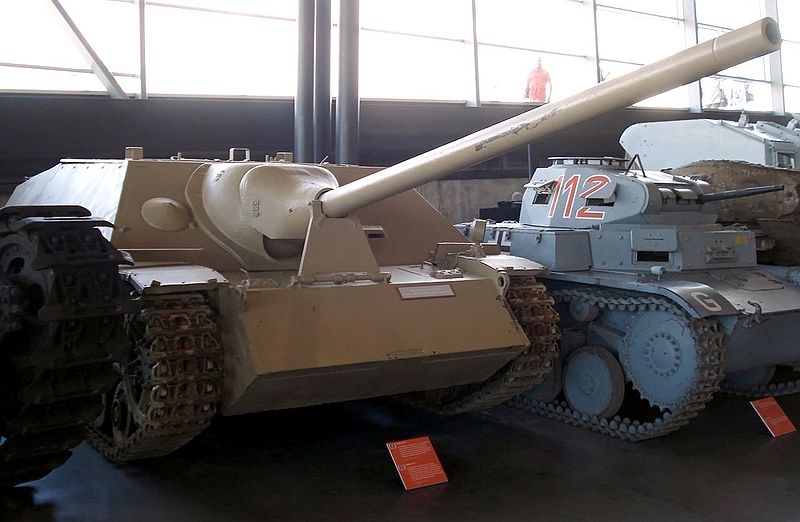
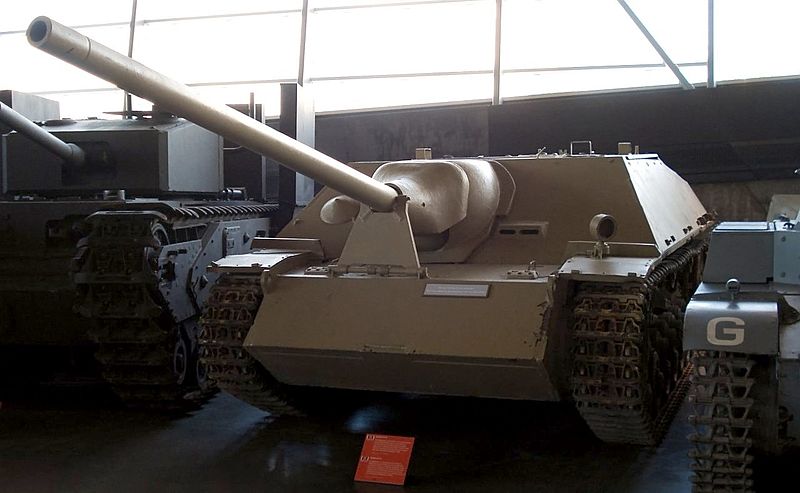


Jagdpanzer IV/70 (Vomag) at the Ottawa War Museum.
Production
The official names of the vehicle were Sd.Kfz.162 – 75 mm L/48 (1944) or Sturmgeschütz neuer Art mit 7.5cm PaK L/48 auf Fahrgestell Pz.Kpfw.IV.
Its famous surname became “Guderian Ente” or “Guderian’s Duck”. The first batch was produced in January 1944, with 30 vehicles. In October 1944, the early production run ended and, in November, a new batch was produced, severely hampered by Allied air raids on Vomag AG and suppliers like Zahnradfabrik AG in Friedrichshafen. The production rate dropped well below the plans. Peak production occurred in July (with 140 vehicles) and June (with 120). In August 1944, the transition began to the long-barreled 7.5 cm KwK. 42 L/70 gun. A total of 769 short-barrel and 1208 long-barreled versions – 930 Jagdpanzer IV/70(V) and 278 Jagdpanzer IV/70(A) – were built until March-April 1945. Suppliers were Witkowitzer Bergbau und Eisenhuetten Gewerkschaft, the arms company Rheinmetall-Borsig and Seitz.
Operational history
“Guderian’s ducks” were made famous by their battle performances as tank hunters, their ability to take punishment and extremely low profile. However, they performed poorly when used as ad hoc assault guns in support of the infantry, due to the nature of their rounds. Guderian himself, as the Inspector-General of the Panzertruppen, was not enthusiastic about these, claiming that the cheaper StuG III, similarly armed, was sufficient for the job and wanted to increase production instead. But Hitler remained adamant about the succession of the Panzer IV with the Jagdpanzer IV, until it was shown sustaining production of the former was a better decision. Due to these hesitations, production started much later than expected, and with a much slower pace than anticipated. The Allied bombing campaign was also involved in disrupting the production. However, despite this and being a self-propelled gun, thus lacking traverse, the Jagdpanzer IV was liked by its crews for its firepower, protection and reliability. As a difficult target, it was excellent on the defensive and, with the 75 mm L/70, it was able to destroy all Allied tanks, except the Soviet IS-2, from a safe distances.
Jagdpanzer IV at the Panzermuseum Munster in 2010
The Jagdpanzer IV was painted in accordance to the 1943 directives, all sand, but with two or three-color patterns, generally sprayed red-brown and olive green. However, in a few instances, a basic monochrome Wehrmacht olive was applied. In winter, a washable white or lime paint was applied all over the superstructure. Identification inside divisions called for three-digit tactical numbers. The first represented the company in the division, the second the platoon and its composition, and the third the individual tank. This number was usually painted in reddish or black paint, often with snow-white borders for better contrast with the camouflage. Crosses were applied to the sides of the hull. Badges were occasionally used in the 4th and 16th Tank Divisions and unit logos were placed on the rear wing and front armor. As a usual practice, crews painted snow-white rings on the gun barrel for each kill.
Eastern Front
The first production Jagdpanzer IVs arrived in combat units in the spring of 1944. Typically, they were part of organic Panzerjager Abteilungs, or tank destroyer battalions, formed in accordance with the schedule KStN 1149 Ausf.A (February 1, 1944). Each division included two combat companies of 14 vehicles, with three command vehicles for the headquarters company of the division, for a total of 31 Jagdpanzer IVs. Each company of a Panzer Division had only 10 Jagdpanzer IVs (three platoons of three vehicles plus a command tank), for a total of 22 vehicles. In May 1944, the 49th Division, 4th Armored Division and 5th Panzer Division on the Eastern Front received Abteilungens of Jagdpanzers IVs.
In March, 17 the XIIth Panzer Lehr Division received 31 Jagdpanzer IVs. The 2nd Armored Division received 21 others in April. The Xth Panzer-Lehr-Division was also planned to integrate a company of Jagdtigers and one of Jagdpanzer IVs.
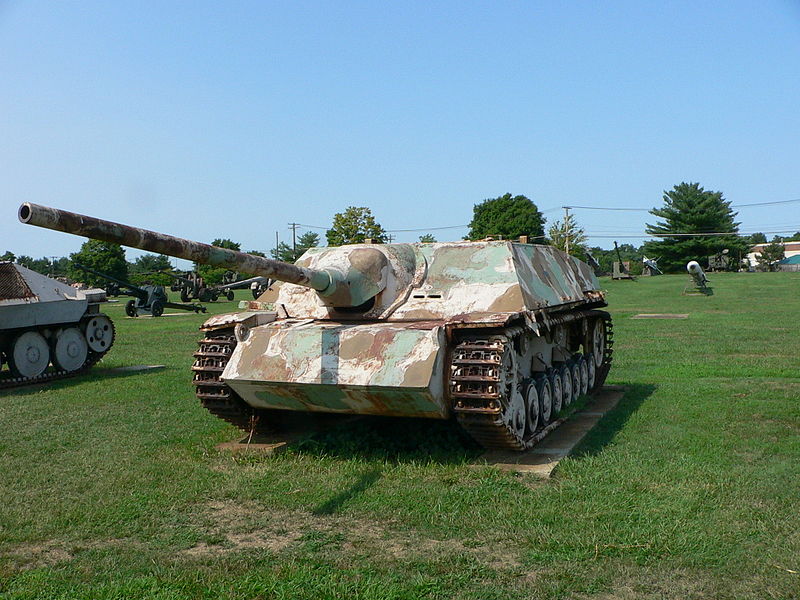
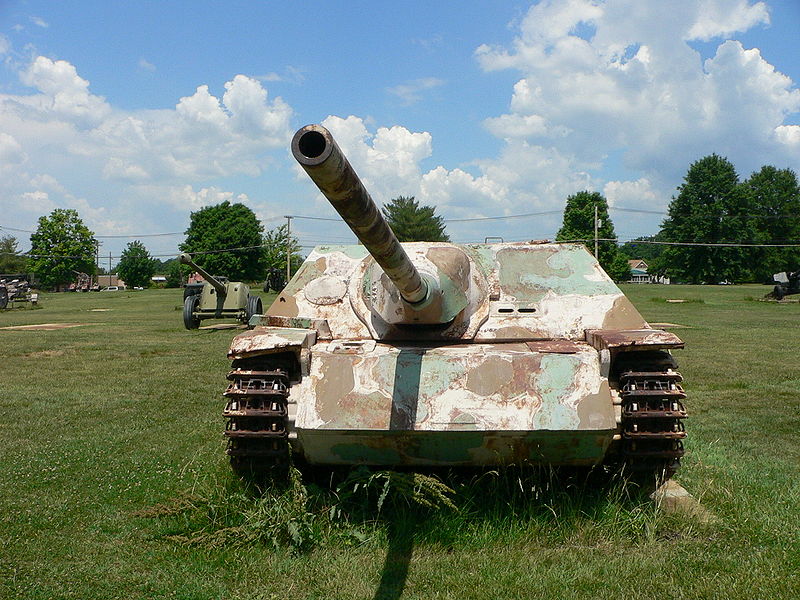


Jagdpanzer IV/70(V) preserved at the US Army Ordnance Aberdeen Proving Grounds museum, later displaced to Fort Lee, outside Petersburg, Virginia.
Italy
In April 1944, the 3rd Battalion and the Parachute Panzer Division «Hermann Goring» were reformed in line with the staffing KStN 1106d and 1155d of 01.11.1943. They received 21 Jagdpanzer IVs from the Army Reserve Division, seeing heavy fighting in Italy. A third tank destroyer battalion was allocated to the XVth Grenadier Division. On April 25, the «Hermann Goring» division was allocated a new commander, and 21 Jagdpanzer IVs. It was deployed in Tivoli. The Tenth Company, under the command of Oberleutnant Karl-Heinz Hering (a cousin of Field Marshal Hermann Goering), held the front to the south of Livorno. On May 27, a skirmish occurred with Shermans of the U.S. Army. Three Shermans were destroyed without losses for the Abteilung. In July, the 15th Division was filmed in Florence, Bologna, departing from the front to the east. On July 22, it was redeployed around Breslau-Gross Masselvits and received 31 Jagdpanzer IVs, while another tank battalion was left in Italy. On 26 July, it was deployed in Warsaw from the station Hernpoch and then in the Otwock area. They were successful, but the side skirts proved to constantly cling to buildings and trees.
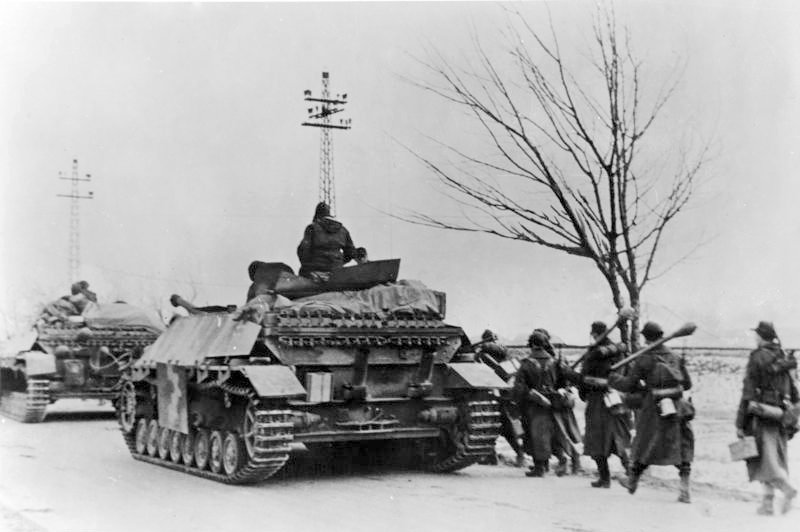

Jagdpanzer IVs and Panzer Grenadiers en route to the front, Hungary, fall 1944.
France
On June 6, 1944, there were 62 Jagdpanzer IVs available, 31 for the Panzer-Lehr-Division, 21 for the 2nd Armored Division and 10 in the XIIth Division SS «Hitlerjugend». The XIIth SS Panzerdivision in France was formed on 26 April of the same year, with an initial batch of 10 Jagdpanzer IVs, but then another batch of 11 joined in, which saw action in July 1944 after the Allied landings in Normandy. Tank destroyers of the 12th SS Panzer Division SS had a battalion commanded by Sturmbannfuhrer Hanrayh. His subordinate, Oberscharführer SS Roy Rudolph (12th Abt.) was considered the best Jagdpanzer IV commander, achieving ace status with 36 kills in total. This fame was acquired in the first days of the fighting in Normandy. In the Emeville area in July 20, 1944, he single-handedly knocked out several American Shermans. On August 10, he went into action against the First Polish Armoured Division, knocking out eleven Polish Shermans for only seven casualties in his platoon. Roy was killed in action during the Battle of the Bulge, shot by a US sniper while scanning out of the cupola on December 17, 1944. Jagdpanzer IVs of the 12th Division indeed played a significant role during the German breakthrough from the Falaise pocket and during the battle of the Bulge, were most were destroyed.
Jagdpanzer IV preserved at the Kubinka museum.
By late 1944, Jagdpanzer IV/70 equipped with the long-barreled 75 mm (2.95 in) guns arrived in growing numbers, replacing losses and being even more efficient as tank hunters. But, on paper, on December 30, 1944, active units possessed a total of only 268 tank destroyers of the Jagdpanzer IV type, of which 209 were deployed on the Eastern front and 59 on the Western front. But only 174 were serviceable at any time.
Today, a Jagdpanzer IV (0-Serie) can be seen at the Saumur Armour Museum in France with two Jagdpanzer IVs (L/48) and the only surviving Jagdpanzer IV/70(A). Two Jagdpanzer IVs (L/48) are preserved at the Panzermuseum Munster in Germany and in the Panzermuseum Thun in Switzerland. A single one is on display in Syria, one of the few sold to this country and involved in the 1967 war. A model IV/70(V) is displayed in Shrivenham in England, another in Sofia in Bulgaria, one at the Patton Museum in Fort Knox, USA and another at the Aberdeen Proving Grounds in Maryland in USA. There is also one in the War Museum in Ottawa in Canada and another in Kubinka in Russia. The legacy of this type can be clearly seen in the Cold War West German Kanonenjagdpanzer 90 of the 1960s and in the 1970s Swedish Strv 103.
Links and resources about the Jagdpanzer IV
The Jagdpanzer IV on Wikipedia
On Achtung Panzer
A website dedicated to the Panzer IV and its variants
1944 video footage about the Jagdpanzer IV/70
Jagdpanzer IV specificaitons |
|
| Dimensions (L-W-H) | 8.5 x 3.17 x 1.85 m (27.1 x 10.5 x 6.1 ft) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 25.8 tons (51,600 lbs) |
| Armament | 7.5 cm (2.95 in) Pak 39 L/48 or Pak 42 L/70 (55 rounds) 7.9 mm (0.31 in) MG 42, 600 rounds |
| Armor | 10 to 80 mm (0.39 – 3.15 in) |
| Crew | 4 (driver, commander, gunner, loader) |
| Propulsion | Maybach HL 120 TRM, 300 hp (221 kW), 11.63 hp/ton |
| Speed | 40 km/h (25 mph) |
| Suspension | Leaf springs |
| Operational range | 210 km (130 mi) |
| Total production | About 1,977 |

Jagdpanzer IV of the 0-series, examined by Guderian in January 1944.

Jagdpanzer IV, Kampfgruppe Von Luck, Normandy, June 1944.

Jagdpanzer IV from the 33rd Panzer-Abteilung, 15th Panzer Division, Italy, 1944.

Captured Russian Jagdpanzer IV, 3rd Ukrainian Front, Hungary, March 1945.

Jagdpanzer IV L/48, Germany, April 1945.
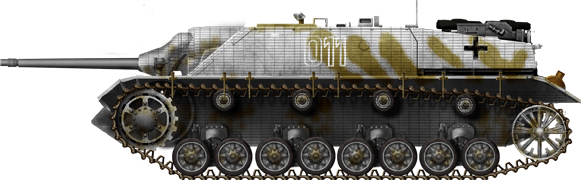
Jagdpanzer IV L/48 in winter camouflage, 53rd Panzerjäger Abteilung, 5th Panzer Division, East Prussia, January 1945.

Jagdpanzer IV L/48, 3rd SS Panzerjäger Abteilung, 3rd SS Panzer Division, Hungary, March 1945.
.png)
Jagdpanzer IV/70(A), Sd.Kfz.162/1 Zwischenlösung, in support of the 352nd Volksgrenadier division, Ardennes, 1944.
Compogne-Belgium44.png)
Jagdpanzer IV/70(A) from the 116th Panzer Division, Compogne, Belgium, fall 1944.
-Ardennes1944.png)
Jagdpanzer IV/70(A) in the Ardennes, battle of the Bulge, December 1944.
early-winter-paint1945.png)
Early type Jagdpanzer IV/70(V) in winter camouflage, Hungary, possibly January 1945.
_late-type-1945.png)
Late type Jagdpanzer IV/70(V) based on the Panzer IV Ausf.H, 13th Panzer Division, Hungary, January 1945.
_Ausf-H-late.png)
Jagdpanzer IV/70(V), late version, 1st SS Panzer Division, Hungary, 1945.
-late-1945.png)
Jagdpanzer IV/70(V), late version, 13th Panzer Division, Hungary, January 1945.

WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com
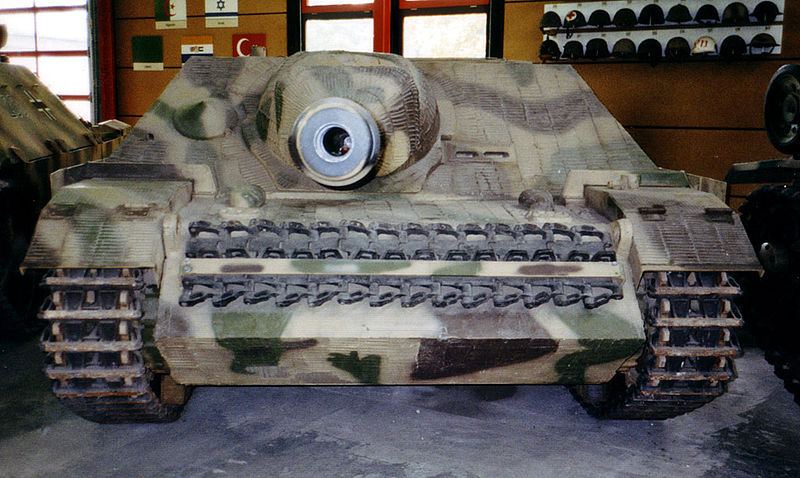




_Saumur-museum2.JPG)



