The origin: The Großtraktor
The very roots of the Neubaufahrzeug (literally: “New Construction Vehicle”) are connected to the arrival of Hitler as the new head of state, and the desire to have, as quickly as possible, a suitable heavy tank, both for the army needs and for propaganda purposes. It had to be a symbol of the renewal of the German Army and was conceived in quite a hurry. Its inspirations can be traced back to the British multi-turreted prototype Vickers A1E1 Independent, which also inspired the the Soviet T-28 and T-35. The former was under intense scrutiny when the Reichswehr decided, in 1926, to give a contract to Rheinmetall-Borsig, MAN, Daimler-Benz and Krupp for the Reichswehr Großtraktor.

Reichswehr Großtraktor built by Krupp undergoing trials (Bundesarchiv)
This was a disguise designation, used to cover up tank development, which was forbidden under the Versailles treaty. Tests were performed at Panzertruppenschule KAMA, the gunnery and testing grounds at Kazan, in the USSR, and Oberstleutenant Malbrandt supervised the tests. This high security proving ground was part of the joint Red Army and Reichswehr training and testing cooperation, born from the treaty of Rapallo signed in 1922. Two prototypes of Daimler Benz’s Grosstraktor I were tested in 1929, showing transmission problems. Two others, Rheninmetall-Borsig’s Großtraktor II, were also tested in 1929 and modified for new tests in 1931. After a new campaign of trials, the four prototypes were given to the 1st Panzer Division for the 1935 maneuvers. Since they had been plagued by many problems, they ended as monuments outside training camps or practice targets for gunners, but paved the way for the upcoming Neubaufahrzeug.
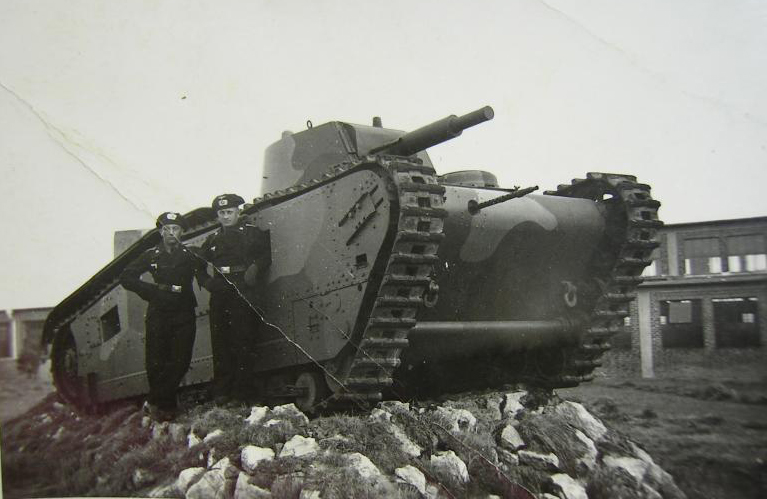

A Großtraktor turned into a monument with 2 german trainees. (Source N/A)
Pz.Kpfw. Nb.Fz.V and VI
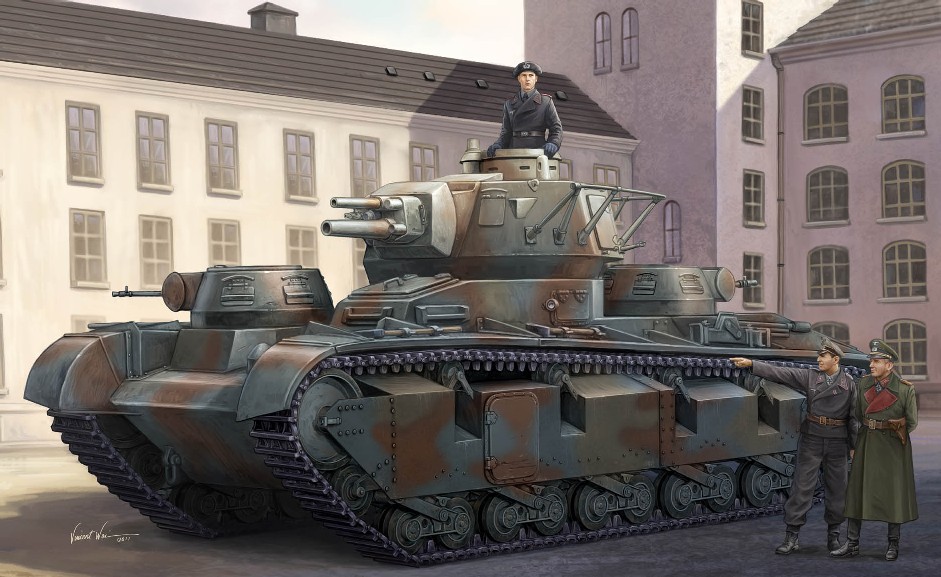
Only two prototypes were built at first, one by Krupp – Model A, and the other by Rheinmetall-Borsig – Model B, and they differed only by their gun arrangement. The 75 mm (2.95 in) KwK L/24 main gun and secondary 37 mm (1.46 in) KwK L/45 was mounted coaxially in a single mantlet on the Krupp prototype and in vertical tandem on the Rheinmetall one. The two secondary turrets, equipped with cal.303 (7.7 mm) machine-guns, were borrowed from the Panzer I, then in development, but modified in order to fit. The Rheinmetall version was named Pz.Kpfw. Nb.Fz. V, and the Krupp vehicles were named Pz.Kpfw. Nb.Fz. VI. Once the two designs were ready, the first two prototypes were built in 1933-34 (N°1 and 2) and three others (N°3, 4 and 5) in 1934-36.
Design of the Neubaufahrzeug
The first two tanks were built in mild steel, with partially welded hulls. Final assembly (fittings and turrets) was performed at Krupp. The first one had the original Rheinmetall turret with the tandem guns (the 37 mm/1.46 in Tankkanone L/45 was installed over the 75 mm/2.95 in KwK L/24) and a horse-shoe FuG turret antenna. All the other four were given the Krupp turret (coaxial guns). There was also a project of conversion to a Nebel Panzer, armed with 105 mm (4.13 in) gun firing smoke rounds, which never materialized. The two secondary turrets were mounted in a lozenge configuration, one on the front left and the other one on the right rear. The driver compartment was next to the front turret, with the main fighting compartment behind. There were two rear hatches for the original BMW engine (Type A), replaced for the four others by a more powerful 300 hp gasoline Maybach HL 108 TR fed with 457 liters of fuel.
Transmission was done by a crash gearbox, 5 speed forward, no reverse. The suspension system consisted of modified coil (leaf) springs coupled with Christie type torsion arms, attached to a set of five bogies with paired road wheels. The front single road wheel was suspended independently, like on the British A1E1 and Russian T-28. They were protected by side skirts with mud chutes in échelon (under each return roller), with two access doors to the suspension. The turret also had two large, one piece access side hatches. The commander cupola was at the turret rear end. Provision for ammunition was 80 rounds for the main gun, 50 for the coaxial 37 mm (1.46 in), and around 6000 for the two MG 34 machine-guns. Armor was not particularly thicker than other Panzers of the time, just enough to provide minimal protection against infantry weapons, light AT guns and shrapnel.
Active service
Soon after delivery, the three late prototypes were extensively tested at the proving grounds at Putloss, while the first two took part in army maneuvers. However, by the end of 1936, it was decided to cancel all further development of the series, priority being given to the Panzer IV. The main tactic devised, notably by Heinz Guderian, favored mobility over firepower, which was as the very core of the Blitzkrieg. This condemned these vehicles, which soon became the “white elephants” of the Wehrmacht, displayed in all propaganda displays, shows and newsreels, starting with the International Automobile Exposition in Berlin, 1939. Another of these mediatic coups was that a platoon consisting of all three late prototypes, named Panzerzug Horstmann, after its commander, Lieutnant Hans Hortsmann, was deployed in Norway, notably to give the impression of a larger production. Similar disinformation operations had been also successfully performed with the Heinkel 100 fighter, despite the appearance in Spain of the Bf 109. The three were landed at Oslo harbor on April, 19, 1940 and took part in local operations. Although handicapped by their speed, they were still an impressive sight, and by far the most heavily armed German tanks fielded there, combining the firepower of a Panzer IV and two Panzer Is in a single package. This unit was later posted at Akershus Fortress (Oslo) in Norway, in 1941 and their fate is unclear, although they were eventually captured in Norway by 1945 and scrapped afterwards. The two others seem to have taken part in operations in Ukraine and Romania.
Neubaufahrzeug specifications |
|
| Dimensions | 6.6 x 2.19 x 2.98 m (21.8×7.2×9.9 ft) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 23.41 tons |
| Crew | 6 (commander, driver, loader, 3 gunners) |
| Armament | 75 mm (2.95 in) KwK L/24 gun 37 mm (1.46 in) KwK L/45 2 or 3 x7.92 mm (0.31 in) MG 34s |
| Armor | 13 to 20 mm (0.51-0.79 in) |
| Propulsion | 290 hp BMW Va or a 300 hp Maybach HL 108 TR |
| Suspension | Leaf spring system |
| Speed (road) | 25-30 km/h (16-18 mph) |
| Range (road) | 120 km (75 mi) |
| Production | 5 prototypes |

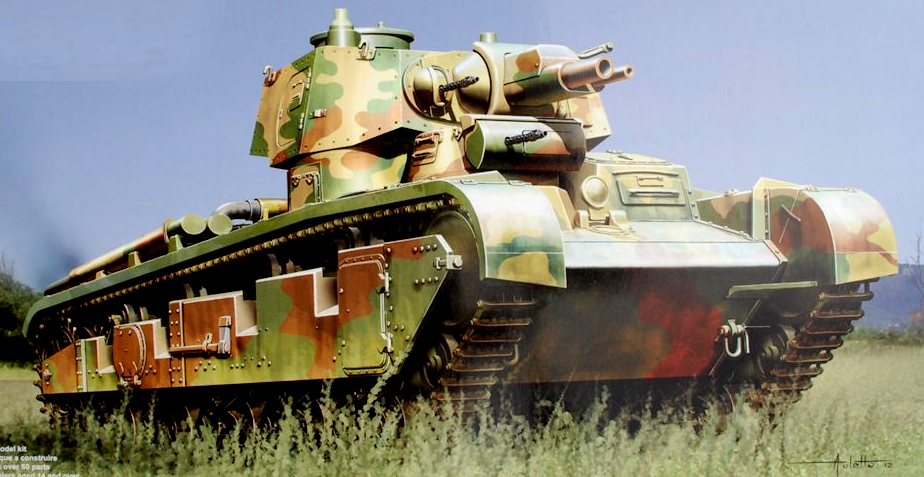
Neubaufahrzeug number 1 (Type A) was the only fitted with the original Rheinmetall-Borsig turret, showing an early large FuG horse-shoe radio antenna. The large size of the tank was well suited for a platoon commander vehicle. The three-tone camouflage was usual by 1937-38, seen here used in maneuvers at Panzertruppenschule Putlos. Their fate during the war is unsure. Reports seem to point to the fact that the first two vehicles served in the Balkans in March-April 1941, and were shipped to Army Group South, the Romanian sector. In the summer of the same year photos of one of these was taken at Dubno (28 of June, western Ukraine, during operation Barbarossa), with the usual dunkelgrau livery and a triple X as unit marking on the turret.
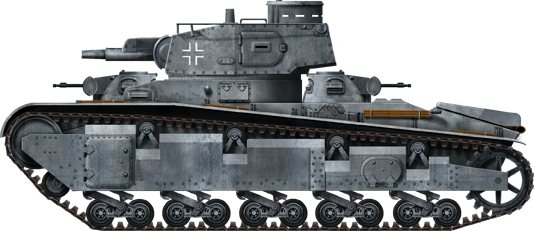
Nb.Fz.VI, or Type B, with the Krupp turret and operational markings, part of the Hortsman platoon, also comprising two other “B” tanks. Number 8, Vaerwaagen, southern Norway, late April 1940. They were later stationed near the Oslo fortress during most of the war.
Neubaufahrzeug gallery
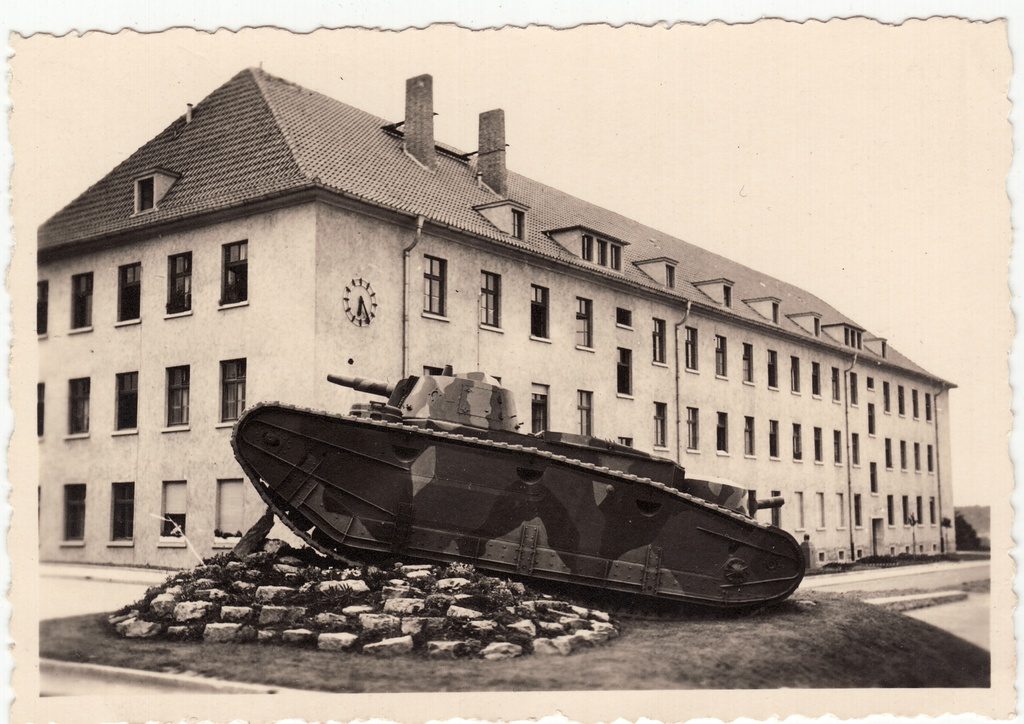

Another Großtraktor turned into a monument. Photo: – forum.valka.cz
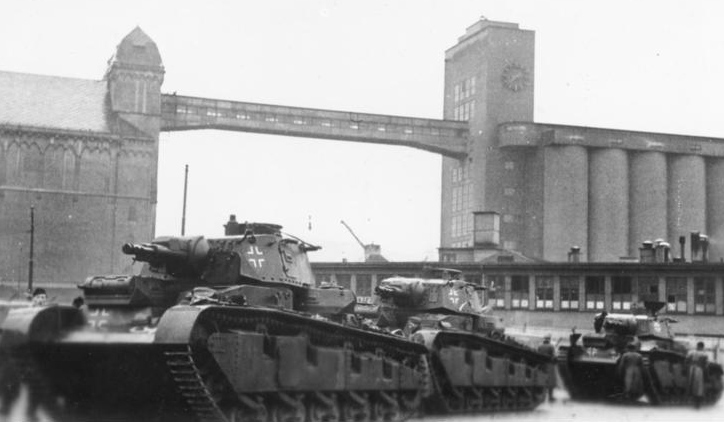

Neubaufahrzeug in Norway, Olso harbor, 19 March 1940

Neubaufahrzeug Type B (Pz.Kpfw. Nb.Fz. VI) in Norway, April 1940 – Credits: Bundesarchiv.

Neubaufahrzeug Type B being repaired – Credits: Bundesarchiv.


Originally published before 1 December 2014

WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

